What are Fixed income?
A Bond is a debt instrument that is a contract between the issuer of debt and the debt holder (also called "investor"). Bonds must have specifically defined maturity dates, interest rates, and other benefits. Also, interest payment dates and redemption dates/principal payment dates must be specified at time the bond is issued in addition to the maturity period. Bonds are transferable and can be traded.
Bond issuers are borrowing from the bond buyer, so the issuer is the "debtor" while the buyer is the "lender" or "creditor." Being debt, bonds are unlike equities or common stock, where investors buy shares which represent ownership in a company.
“Debt instrument” is a broadly used term. But, in Thailand “bond” is often used to refer to debt instruments issued by governments or state enterprises, while “debentures” are most often issued by private companies. In other countries, "bond" may refer to debt issued by both government and private entities, while debt instruments unsecured by collateral are referred to as "debentures."
Types of Fixed income
Advantages of debt instruments
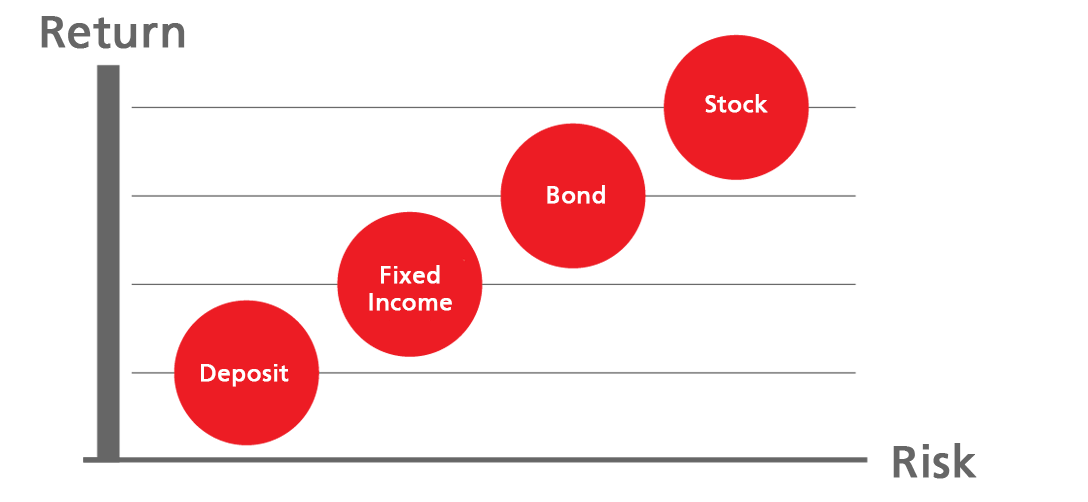
Comparative Chart
Return / Risk
Of each type of investment.
The correlation of
bond prices and bond yields.
bond prices and bond yields.

How to Apply


